Where Is Thin Skin Found
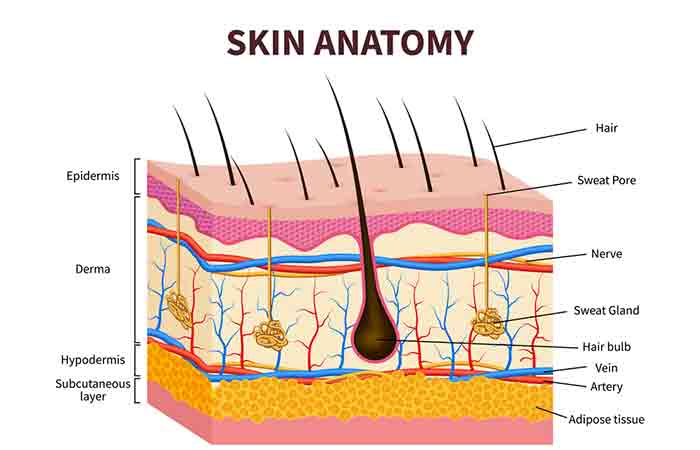
The first layer of defense for your body confronting environmental aggressors, germs, and diseases is your skin. Y'all have varying levels of thick and thin skin all over your body. The skin has three layers, and it generally consists of sebaceous glands and hair follicles. The thickness of the layers and their components varies across the body. In this article, we take illustrated the difference between thick and thin skin. Proceed reading to learn more!
What Is Thin Pare?
iStock
Thin pare has a thinner epidermis (top layer)and lacks the stratum lucidum layer. The epidermis has total v layers (one):
- Stratum basale or Stratum germinativum: It is the deepest layer of the epidermis and contains melanocytes (cells that produce melanin).
- Stratum spinosum: It has 8-10 cells layers and contains the dendritic cells (a type of immune cells).
- Stratum granulosum: It has 3-five cell layers and contains the glycolipids that continue the skin cells stuck.
- Stratum lucidum: It contains 2-3 cell layers and is but found in thick peel in the soles and palms.
- Stratum corneum: It is the uppermost skin layer and has 20-30 cell layers made of keratin and expressionless keratinocytes (cells that produce keratin).
Thin pare is found all over the body except the hands, arms, and feet. The heart area, especially the eyelids, has the thinnest pare.
Did You Know?
The upper back skin is the thickest (considering the thickness of the dermis) only is considered thin pare equally it has a thinner epidermis.
Now, allow's empathize what thick skin is.
What Is Thick Skin?
iStock
Dissimilar thin skin, thick peel has all five epidermis layers and is mainly present in areas that receive the most friction, like the fingertips, palms, and soles. Thick peel is hairless and does not contain sebaceous glands and apocrine sweat glands as information technology opens in the hair follicle.
Here is a brief overview and comparison between the structure of thin and thick pare.
Thick Skin Vs. Thin Skin
Shutterstock
| Appearance And Structure | Thick Pare | Thin Skin |
| Dermis (2d layer) | Has a sparse dermis. | Has a thick dermis. |
| Dermal Papillae | Has dermal papillae that consist of mesenchymal cells to regulate pilus growth. | Has more prominent dermal papillae. |
| Epidermis | Has v layers in the epidermis. | Has only four layers in the epidermis. |
| Sensory Receptors | Has dense sensory receptors. | Has scattered sensory receptors. |
| Sweat Glands | Has only eccrine sweat glands that release water to cool down skin's surface. | Has both eccrine and apocrine glands (secretes fatty sweat). |
| Hair Follicles | Does not have any hair follicles. | Has pilus follicles. |
| Sebaceous Gland | No sebaceous glands. | Contains sebaceous glands. |
| Arrector Pili Muscles | Does non contain arrector pili muscles (that causes goosebumps). | Has arrector pili muscles. |
Apart from these differences, thick and sparse skin take unlike functions.
Thin skin contains:
- Pilus follicles continued to different glands and muscles help to regulate torso temperature and repair wounds (ii).
- Sebaceous glands produce sebum to keep the skin nourished, moisturized, and protected.
- Sweat glands regulate body temperature.
Thick pare:
- Prevents damage to areas that are exposed to maximum friction.
- Has eccrine sweat glands that help regulate body temperature.
In A Nutshell
Our body skin has different thickness levels, depending on the thickness of the epidermis. The peel is thick on the palms and feet soles, where the skin is exposed to maximum friction. In contrast, the balance of the torso parts have sparse skin and contains hair follicles and sebaceous glands. The homo skin has a complex construction that comprises cells, nerves, and muscles and the different thickness of peel on our body helps maintain unlike trunk functions. We hope this commodity has helped y'all understand the deviation between thin and thick skin and the office they perform.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does pare thicken with age?
No, the outer layer of the peel tends to become thinner with age (3).
Is thick pare genetic?
Yes, thick skin could exist seen in certain skin atmospheric condition that are a result of genetic mutations (four).
What is the best vitamin for the pare?
Vitamins D, A, C, and East are all essential for developing and maintaining a salubrious pare bulwark (5).
Is milk expert for skin?
Yep, milk is rich in proteins and is known to have antibacterial and antioxidant backdrop that can help heal and restore your natural skin barrier (6).
Primal Takeaways
- Thick skin has v epidermis layers and mainly occurs in areas that receive the most friction, similar the fingertips, palms, and soles.
Sparse skin is present in all trunk parts except the easily, arms, and anxiety. Information technology has a thinner top layer and does non have the stratum lucidum layer. - Thick skin is hairless and does not contain sebaceous glands and apocrine sweat glands, whereas thin skin contains hair follicles and eccrine and apocrine sweat glands.
- The skin on the palms and soles is the thickest, and the peel under the eyes is the thinnest.
Sources
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified data from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to larn more.
- Anatomy Skin (Integument) Epidermis
https://world wide web.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470464/ - Histology Hair and Follicle
https://world wide web.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532929/ - Characteristics of the Aging Pare – PMC
https://world wide web.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3840548/ - 25 How to be thick-skinned: genetic disorders of skin and smash – PMC
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/manufactures/PMC1570930/ - Discovering the link betwixt nutrition and skin aging – PMC
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3583891/#:~:text=Vitamin%20D,25%2Ddihydroxy%20vitamin%20D3%20synthesis - Milk Proteins—Their Biological Activities and Use in Cosmetics and Dermatology – PMC
https://world wide web.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8197926/
Was this article helpful?
The following ii tabs change content below.
- Author

Ramona is an editor at StyleCraze. Prior to that, she authored over 200 articles on pare and hair care. She... more
Where Is Thin Skin Found,
Source: https://www.stylecraze.com/articles/thin-and-thick-skin/
Posted by: mcglonelibse1995.blogspot.com




0 Response to "Where Is Thin Skin Found"
Post a Comment